Innovation with PVC Pipes is reshaping how people perceive one of the most versatile building materials in modern design. Mention PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) pipes to most people, and what often comes to mind are their long-standing roles in plumbing systems, water supply lines, and agricultural irrigation. For decades, these pipes have been valued in construction and farming for their durability, resistance to corrosion, and cost-effectiveness. Yet their utility extends far beyond such conventional applications.
Across India—whether in the bustling commercial streets of Kolkata, the culturally rich districts of Jaipur, or the eco-conscious regions of Assam and Odisha—PVC pipes are becoming central to design innovation. Architects and artists are increasingly harnessing the versatility, affordability, and structural strength of PVC materials to create functional architecture, contemporary public art installations, and even eco-friendly urban infrastructure. These creative applications bridge the gap between engineering practicality and aesthetic excitement, reshaping how spaces are imagined and built.
Why PVC Pipes Work for Creative Architecture & Art
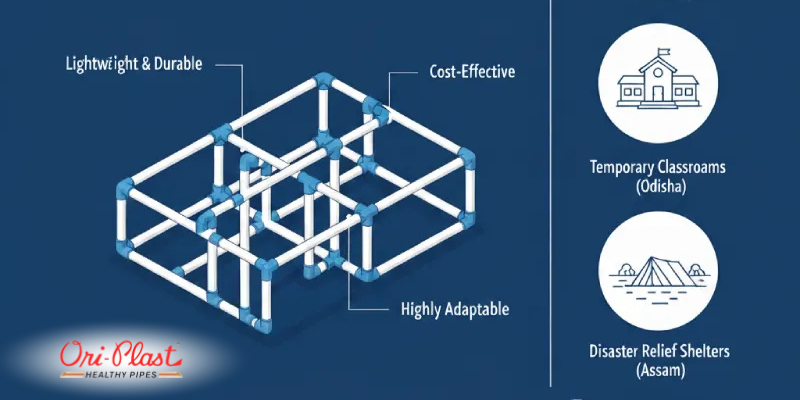
PVC pipes offer a combination of properties that make them prime candidates for unconventional applications:- Lightweight yet durable – Despite being light enough for easy handling, PVC pipes maintain impressive tensile strength. They can support structural elements when designed correctly, making them useful for lightweight frameworks, temporary pavilions, and event structures.
- Cost-Effective – Compared to materials like aluminum, steel, or hardwood, PVC pipes are far more affordable. This makes them ideal for projects with budget constraints yet high creative ambitions.
- Weather Resistant – PVC’s natural resistance to corrosion, rust, rotting, and UV degradation ensures long-term performance outdoors without requiring constant upkeep.
- Highly Adaptable – PVC can be cut, bent using heating techniques, drilled, or painted to match design needs. It pairs well with modern adhesives, fittings, and modular connectors.
- Eco-Friendly Potential – While plastic materials often raise environmental concerns, PVC pipes can be reused in different projects, recycled, and incorporated into designs that minimize waste compared to disposable materials.
Architectural Innovations with PVC Pipes
Structural Design & Modular Builds
Forward-thinking architects are reimagining PVC pipes as load-bearing and shape-defining components for modern structures. Using standardized pipe lengths and connector joints, structures can be assembled, disassembled, and transported with ease. Examples include:- Event Canopies – Large, open-sided tents supported by PVC frames for festivals in Guwahati and design expos in Jaipur.
- Temporary Classrooms – In rural Odisha, modular PVC pipe structures provide cost-effective classrooms and community halls in areas needing rapid construction.
- Disaster Relief Shelters – PVC pipes’ portability and ease of assembly make them indispensable for building shelters after floods or cyclones, common in Assam and coastal Odisha.
Water Management in Sustainable Architecture
One of PVC’s traditional strengths—water conveyance—is finding innovative expression in sustainable architecture. Architects integrate PVC piping into building frameworks, not only to manage plumbing and wastewater but also to promote eco-conscious water cycles. Notable uses:- Rainwater Harvesting – PVC pipes serve as collection and distribution channels for harvesting systems on rooftops, diverting rainwater to storage tanks for later use in landscaping or sanitation.
- Green Walls with Irrigation – Vertical gardens in Kolkata’s commercial buildings use embedded PVC irrigation lines to keep vegetation healthy while conserving water.
Facade Creativity and Ventilation Structures
PVC pipes are increasingly forming part of striking building facades. By cutting and arranging pipes in patterns, architects achieve dynamic textures that function both aesthetically and practically.- Sun & Wind Screens – Cylindrical arrangements filter sunlight while promoting ventilation in buildings across Jaipur’s hot climate.
- Interactive LED Panels – In tourist centers, PVC facades embedded with LEDs create engaging light shows that enhance a building’s visibility and appeal.
Artistic Expressions with PVC Pipes
Large-Scale Sculptural Installations
The range of diameters available for PVC pipes allows artists to construct sculptures with dramatic curves, intricate latticework, or geometric motifs. PVC’s ability to be painted or coated expands its surface appeal, enabling vibrant outdoor installations.- Community Sculptures in Assam – Artists create thematic pieces representing local culture and wildlife using PVC frameworks covered with environmentally friendly paints.
- Festival Art in Odisha – Temporary installations for cultural fairs use PVC compositions that can be quickly dismantled and reused for future events.
DIY Home and Interior Art Projects
PVC pipes’ affordability and accessibility make them perfect for home-based creatives and interior designers. Furniture, decor, and functional art projects can be crafted with minimal tools. Examples include:- Lamp stands and chandelier frameworks.
- Custom shelving and plant holders painted in vibrant colors.
- Decorative room dividers with perforated patterns for privacy and light play.
Public Art and Urban Beautification
Cities increasingly use PVC for urban installations that withstand wear, weather, and public interaction.- Interactive Play Installations – Parks in Guwahati have play tunnels built using large PVC rings.
- Urban Seating Solutions – Benches in public plazas designed with PVC frameworks combine durability with a contemporary aesthetic.
Environmental and Economic Advantages
PVC’s use in creative projects addresses sustainability concerns by substituting heavier, more energy-intensive materials like steel, aluminum, and concrete. By recycling PVC components from plumbing projects or using offcuts creatively, design teams reduce waste. Economic benefits are equally impactful:- Lower material procurement costs compared to conventional architectural metals.
- Reduced transport costs due to lightweight nature.
- Minimal maintenance costs thanks to durability and corrosion resistance.
Case Studies Showcasing PVC Innovation
- Modular Pavilion in Kolkata Designed for an art festival, the pavilion uses a grid of PVC pipes joined with quick-connect fittings. The structure can be dismantled and transported to other venues, minimizing long-term setup costs.
- Illuminated Facade in Jaipur A commercial complex integrated PVC pipe arrays filled with LED lighting, creating a pulsating wall of color during evening hours.
- Urban Seating in Guwahati Public benches constructed from PVC pipe frames withstand monsoon rains and require no annual painting like traditional metal counterparts.
Implementation Guide for Architects & Artists
- Material Selection – Use thicker diameter PVC for structural roles and thinner diameters for decorative elements.
- Fittings & Connectors – Choose between solvent welding, mechanical fittings, or modular couplers depending on permanence.
- Surface Finishing – Protect and beautify with UV-resistant outdoor paints, matte finishes, or vinyl wraps.
- Design for Modularity – Create sections that can be disassembled for maintenance, relocation, or redesign.
- Safety Considerations – Sand exposed edges and treat surfaces to avoid sharpness or brittleness over time.
Conclusion
PVC pipes are transforming from humble infrastructure components into dynamic design tools for architecture and art. Their lightweight durability, cost efficiency, weather resistance, and adaptability to creative shaping make them a natural fit for the evolving demands of modern design thinking. From modular event structures in bustling cities to intricate artworks in rural cultural hubs, from efficient water management systems to eye-catching urban facades, PVC pipes have proven their worth beyond plumbing. Architects and artists alike are discovering how this everyday material can support sustainable practices, reduce costs, and open new channels for creativity. By embracing PVC pipes as a forward-thinking material choice, designers contribute not only to functional excellence but to eco-conscious, budget-friendly, and aesthetically satisfying creations. In a rapidly urbanizing India, the possibilities are vast—from Jaipur’s architectural statements to Assam’s community art. Each project demonstrates how thoughtful, innovative use of PVC turns practicality into beauty, and efficiency into inspiration. Whether planning a pavilion, designing an irrigation-linked green wall, or constructing memorable public art, PVC pipes invite innovation at every turn—proving that the future of design may well be built through the power of versatile, recyclable, and surprisingly elegant everyday materials.FAQ
What makes PVC pipes suitable for architectural use?
PVC pipes are lightweight, durable, resistant to weather, and cost-effective, allowing for versatile structural and decorative applications.Can PVC pipes be used outdoors?
Yes, they are resistant to corrosion and UV light, making them ideal for outdoor installations.Are PVC pipes environmentally friendly?
While PVC is a plastic, its durability and recyclability contribute to sustainable use when managed responsibly.How do artists manipulate PVC pipes for sculptures?
PVC pipes can be cut, bent, and connected into various shapes, and painted to achieve artistic visions.Can PVC pipes support load-bearing structures?
With correct sizing and fittings, PVC pipes can provide structural support for lightweight frameworks.What types of PVC pipes are best for architectural projects?
Schedules 40 and 80 are common due to their strength and availability.How to finish PVC pipes for aesthetics?
They can be painted with suitable sprays or coated with weatherproof finishes.Are there limitations to using PVC pipes in construction?
PVC pipes are not suitable for heavy load-bearing or very high-temperature applications.Can PVC pipes be reused in art installations?
Yes, PVC pipes' modularity allows for easy dismantling and reuse.What size PVC pipes are preferred in art installations?
Sizes vary from small diameters (~½ inch) to larger ones (~6 inches) depending on the scale.How do PVC pipe facades help with energy efficiency?
By providing shade and airflow, they reduce heat gain in buildings.Is special equipment needed to cut PVC pipes?
Basic tools like hacksaws or pipe cutters are sufficient.How durable are PVC pipe water tanks?
PVCTanks can last decades if properly maintained.What are eco-friendly alternatives to PVC?
HDPE pipes and recycled materials are sometimes used.Can PVC pipes be used in artistic lighting setups?
Yes, hollow pipes can house LEDs or be combined with light elements.

